First steps
After going through the Installation section and having installed all the operators, you will now deploy a NiFi cluster and the required dependencies. Afterwards you can verify that it works by querying the REST API.
Setup
Two things need to be installed to create a NiFi cluster:
-
A ZooKeeper cluster for internal use by NiFi
-
The NiFi cluster itself
We will create them in this order, each one is created by applying a manifest file. The operators you just installed will then create the resources according to the manifest.
Apache ZooKeeper
To create a ZooKeeper instance run the following command:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: zookeeper.stackable.tech/v1alpha1
kind: ZookeeperCluster
metadata:
name: simple-zk
spec:
image:
productVersion: 3.8.3
servers:
roleGroups:
default:
replicas: 3
EOFCreate a Znode object:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: zookeeper.stackable.tech/v1alpha1
kind: ZookeeperZnode
metadata:
name: simple-nifi-znode
spec:
clusterRef:
name: simple-zk
EOFThe ZNode makes sure that the NiFi cluster will operate in its own separated directory in ZooKeeper.
Apache NiFi
The NiFi cluster requires authentication. Create a set of credentials for this purpose:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: simple-admin-credentials
stringData:
admin: admin
---
apiVersion: authentication.stackable.tech/v1alpha1
kind: AuthenticationClass
metadata:
name: simple-nifi-users
spec:
provider:
static:
userCredentialsSecret:
name: simple-admin-credentials
EOFFinally create a NiFi instance:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: nifi.stackable.tech/v1alpha1
kind: NifiCluster
metadata:
name: simple-nifi
spec:
image:
productVersion: 1.25.0
clusterConfig:
authentication:
- authenticationClass: simple-nifi-users
listenerClass: external-unstable
sensitiveProperties:
keySecret: nifi-sensitive-property-key
autoGenerate: true
zookeeperConfigMapName: simple-nifi-znode
nodes:
roleGroups:
default:
replicas: 2
EOFVerify that it works
First, make sure all pods are ready:
kubectl wait -l statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name=simple-nifi-node-default-0 \
--for=condition=ready pod --timeout=1200s && \
kubectl wait -l statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name=simple-nifi-node-default-1 \
--for=condition=ready pod --timeout=1200sThen make sure the StatefulSets are ready:
kubectl get statefulsetThe output should show all pods ready:
NAME READY AGE
simple-nifi-node-default 2/2 5m
simple-zk-server-default 3/3 7mCongratulations! You successfully created your first NiFi cluster!
Access the NiFi web interface
You can retrieve the URL for the NiFi cluster web interface via stackablectl or kubectl.
stackablectl
Use the service command of stackablectl to get a list of all available endpoints:
stackablectl stacklet listwhich should return something like this:
PRODUCT NAME NAMESPACE ENDPOINTS EXTRA INFOS nifi simple-nifi default https https://172.18.0.3:32595 zookeeper simple-zk default zk 172.18.0.3:30173
You can also use the json output and parse the endpoint:
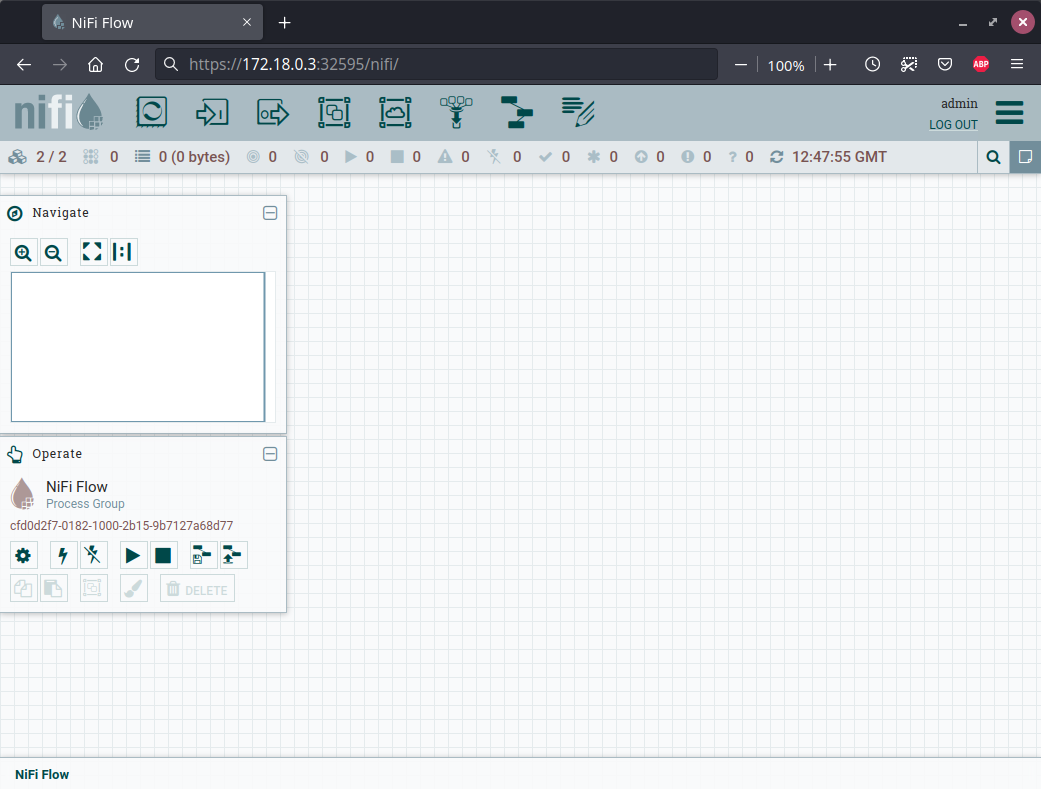
nifi_url=$(stackablectl stacklet ls -o json | jq --raw-output '.[] | select(.name == "simple-nifi") | .endpoints.https')Then connect to https://172.18.0.3:32595/nifi and you should see the NiFi web login. After providing the username admin and password admin you are redirected to the NiFi web interface.
Via kubectl
Extracting the IP and port via kubectl is cumbersome. We recommend using stackablectl instead. The following kubectl commands store their output for further use in a variable and write its content to stdout afterwards. Make sure to run these commands in the same terminal:
nifi_node_name=$(kubectl get endpoints simple-nifi --output=jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].nodeName}') && \
echo "NodeName: $nifi_node_name"which should output a single node name where a NiFi pod is scheduled:
NodeName: kind-workerRetrieve the IP of that node:
nifi_node_ip=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath="{.items[?(@.metadata.name==\"$nifi_node_name\")].status.addresses[?(@.type==\"InternalIP\")].address}") && \
echo "NodeIp: $nifi_node_ip"which should output the internal IP of that node:
NodeIp: 172.18.0.3You might need to replace InternalIP with ExternalIP depending on how you connect to your Kubernetes cluster.
Finally, retrieve the NodePort of the simple-nifi service:
nifi_service_port=$(kubectl get service -o jsonpath="{.items[?(@.metadata.name==\"simple-nifi\")].spec.ports[?(@.name==\"https\")].nodePort}") && \
echo "NodePort: $nifi_service_port"which should output the NodePort:
NodePort: 32595Now build the full URL:
nifi_url="https://$nifi_node_ip:$nifi_service_port" && \
echo "NiFi web interface: $nifi_url"which should output a URL to connect to the NiFi web interface:
NiFi web interface: https://172.18.0.3:32595Then connect to https://172.18.0.3:32595/nifi and you should see the NiFi web login. After providing the username admin and password admin you are redirected to the NiFi web interface.
What’s next
Have a look at the Usage guide page to find out more about the features of the NiFi Operator.